 Vivek Kaul
Vivek Kaul
The Reserve Bank of India(RBI) is doing everything that it can do to stop the rupee from falling against the dollar. Yesterday it announced further measures on that front.
Each bank will now be allowed to borrow only upto 0.5% of its deposits from the RBI at the repo rate. Repo rate is the interest rate at which RBI lends to banks in the short term and it currently stands at 7.25%.
Sometime back the RBI had put an overall limit of Rs 75,000 crore, on the amount of money that banks could borrow from it, at the repo rate. This facility of banks borrowing from the RBI at the repo rate is referred to as the liquidity adjustment facility.
The limit of Rs 75,000 crore worked out to around 1% of total deposits of all banks. Now the borrowing limit has been set at an individual bank level. And each bank cannot borrow more than 0.5% of its deposits from the RBI at the repo rate. This move by the RBI is expected bring down the total quantum of funds available to all banks to Rs 37,000 crore, reports The Economic Times.
In another move the RBI tweaked the amount of money that banks need to maintain as a cash reserve ratio(CRR) on a daily basis. Banks currently need to maintain a CRR of 4% i.e. for every Rs 100 of deposits that the banks have, Rs 4 needs to set aside with the RBI.
Currently the banks need to maintain an average CRR of 4% over a reporting fortnight. On a daily basis this number may vary and can even dip under 4% on some days. So the banks need not maintain a CRR of Rs 4 with the RBI for every Rs 100 of deposits they have, on every day.
They are allowed to maintain a CRR of as low as Rs 2.80 (i.e. 70% of 4%) for every Rs 100 of deposits they have. Of course, this means that on other days, the banks will have to maintain a higher CRR, so as to average 4% over the reporting fortnight.
This gives the banks some amount of flexibility. Money put aside to maintain the CRR does not earn any interest. Hence, if on any given day if the bank is short of funds, it can always run down its CRR instead of borrowing money.
But the RBI has now taken away that flexibility. Effective from July 27, 2013, banks will be required to maintain a minimum daily CRR balance of 99 per cent of the requirement. This means that on any given day the banks need to maintain a CRR of Rs 3.96 (99% of 4%) for every Rs 100 of deposits they have. This number could have earlier fallen to Rs 2.80 for every Rs 100 of deposits. The Economic Times reports that this move is expected to suck out Rs 90,000 crore from the financial system.
With so much money being sucked out of the financial system the idea is to make rupee scarce and hence help increase its value against the dollar. As I write this the rupee is worth 59.24 to a dollar. It had closed at 59.76 to a dollar yesterday. So RBI’s moves have had some impact in the short term, or the chances are that the rupee might have crossed 60 to a dollar again today.
But there are side effects to this as well. Banks can now borrow only a limited amount of money from the RBI under the liquidity adjustment facility at the repo rate of 7.25%. If they have to borrow money beyond that they need to borrow it at the marginal standing facility rate which is at 10.25%. This is three hundred basis points(one basis point is equal to one hundredth of a percentage) higher than the repo rate at 10.25%. Given that, the banks can borrow only a limited amount of money from the RBI at the repo rate. Hence, the marginal standing facility rate has effectively become the repo rate.
As Pratip Chaudhuri, chairman of State Bank of India told Business Standard “Effectively, the repo rate becomes the marginal standing facility rate, and we have to adjust to this new rate regime. The steps show the central bank wants to stabilise the rupee.”
All this suggests an environment of “tight liquidity” in the Indian financial system. What this also means is that instead of borrowing from the RBI at a significantly higher 10.25%, the banks may sell out on the government bonds they have invested in, whenever they need hard cash.
When many banks and financial institutions sell bonds at the same time, bond prices fall. When bond prices fall, the return or yield, for those who bought the bonds at lower prices, goes up. This is because the amount of interest that is paid on these bonds by the government continues to be the same.
And that is precisely what happened today. The return on the 10 year Indian government bond has risen by a whopping 33 basis points to 8.5%. Returns on other bonds have also jumped.
Debt mutual funds which invest in various kinds of bonds have been severely impacted by the recent moves of the RBI. Since bond prices have fallen, debt mutual funds which invest in these bonds have faced significant losses.
In fact, the data for the kind of losses that debt mutual funds will face today, will only become available by late evening. But their performance has been disastrous over the last one month. And things should be no different today.
Many debt funds have lost as much as 5% over the last one month. And these are funds which give investors a return of 8-10% over a period of one year. So RBI has effectively killed the debt fund investors in India.
But then there was nothing else that it could really do. The RBI has been trying to manage one side of the rupee dollar equation. It has been trying to make rupee scarce by sucking it out of the financial system.
The other thing that it could possibly do is to sell dollars and buy rupees. This will lead to there being enough dollars in the market and thus the rupee will not lose value against the dollar. The trouble is that the RBI has only so many dollars and it cannot create them out of thin air (which it can do with rupees). As the following graph tells us very clearly, India does not have enough foreign exchange reserves in comparison to its imports.
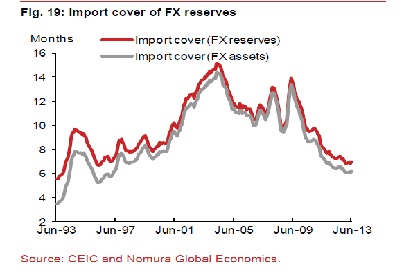
The ratio of foreign exchange reserves divided by imports is a little over six. What this means is that India’s total foreign exchange reserves as of now are good enough to pay for imports of around a little over six months. This is a precarious situation to be in and was only last seen in the 1990s, as is clear from the graph.
The government may be clamping down on gold imports but there are other imports it really doesn’t have much control on. “The commodity intensity of imports is high,” write analysts of Nomura Financial Advisory and Securities in a report titled India: Turbulent Times Ahead. This is because India imports a lot of coal, oil, gas, fertilizer and edible oil. And there is no way that the government can clamp down on the import of these commodities, which are an everyday necessity. Given this, India will continue to need a lot of dollars to import these commodities.
Hence, RBI is not in a situation to sell dollars to control the value of the rupee. So, it has had to resort to taking steps that make the rupee scarce in the financial system.
The trouble is that this has severe negative repercussions on other fronts. Debt fund investors are now reeling under heavy losses. Also, the return on the 10 year bonds has gone up. This means that other borrowers will have to pay higher interest on their loans. Lending to the government is deemed to be the safest form of lending. Given this, returns on other loans need to be higher than the return on lending to the government, to compensate for the greater amount of risk. And this means higher interest rates.
The finance minister P Chidambaram has been calling for lower interest rates to revive economic growth. But he is not going to get them any time soon. The mess is getting messier.
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on July 24, 2013
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek)
Dollar
Why RBI is in a Catch 22 situation when it comes to the rupee
 Vivek Kaul
Vivek Kaul
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will carry out an open market operation and sell government of India bonds worth Rs 12,000 crore today i.e. July 18,2013.
The RBI carries out an open market operation in order to suck out or put in rupees into the financial system. When the RBI needs to suck out rupees from the system it sells government of India bonds, like it is doing today.
Banks and other financial institutions buy these bonds and pay the RBI in rupees, and thus the RBI sucks out rupees from the market.
The rupee has had a tough time against the US dollar lately and had recently touched an all time low of 61.23 to a dollar. By selling bonds, the RBI wants to suck out rupees from the financial system and thus try and ensure that rupee gains value against the dollar.
The RBI has been trying to defend the value of the rupee against the dollar by selling dollars from the foreign exchange reserves that it has. When the RBI sells dollars it leads to a surfeit of dollars in the market and as a result the dollar loses value against the rupee or at least the rupee does not fall as fast as it otherwise would have.
The trouble is that the RBI does not have an unlimited supply of dollars. Unlike the Federal Reserve of United States, the RBI cannot create dollars out of thin air by printing them. In the period of three weeks ending July 5, 2013, as the RBI sold dollars to defend the rupee, the foreign exchange reserves fell by $10.5 billion to $280.17 billion.
At this level India has foreign exchange reserves that are enough to cover around 6.3 months worth of imports. Such low levels of foreign exchange expressed as import cover hasn’t been seen since the early 1990s. Given this, there isn’t much scope for the RBI to sell dollars and hope to control the value of the rupee. It simply doesn’t have enough dollars going around.
Hence, it is trying to control the other end of the equation. It cannot ensure that there are enough dollars going around in the market, so its trying to create a shortage of rupees, by selling government of India bonds.
In fact, as a part of this plan the RBI has also put an overall limit of Rs 75,000 crore, on the amount of money banks can borrow from it, at the repo rate of 7.25%. Repo rate is the interest rate at which RBI lends money to banks in the short term.
Banks can borrow money beyond this limit at what is known as the marginal standing facility rate. This rate has been raised by 200 basis points(one basis point is one hundredth of a percentage) to 10.25%. Hence, borrowing from the RBI has been made more expensive.
A major motive behind this move was to rein in the speculators. As Jehangir Aziz of JP Morgan Chase wrote in The Indian Express “It has been ridiculously cheap over the last month to borrow rupees at the overnight rate, buy dollars and then wait for the exchange rate to crumble. In June, the monthly overnight interest rate was 0.5 per cent and the depreciation 10 per cent.”
Lets understand this through an example. Lets say a speculator borrows Rs 54,000 at a monthly interest rate of 0.5%. This is at a point of time when one dollar is worth Rs 54. He uses this money to buy dollars and ends up buying $1000 (Rs 54,000/54). When he sells rupees to buy dollars it puts pressure on the value of the rupee against the dollar.
After buying dollars, the speculator just sits on it for a month, by the time rupee has depreciated 10% against the dollar and one dollar is worth Rs 59.4(Rs 54 + 10% of Rs 54). He sells the dollars, and gets Rs 59,400($1000 x 60) in return. He needs to repay Rs 54,000 plus a 0.5% interest on it. The rest is profit. This is how speculators had been making money for sometime and thus putting pressure on the rupee.
By making it more expensive to borrow, the RBI hopes to control the speculation and thus ensure that there is lesser pressure on the rupee.
The message that the market seems to have taken from the efforts of the RBI to create a scarcity of rupees is that interest rates are on their way up. The hope is that at higher interest rates foreign investors will bring in more dollars and convert them into rupees and buy Indian bonds. Foreign investors have sold off bonds worth $8.4 billion since their peak so far this year.
When foreign investors sell bonds they get paid in rupees. They sell these rupees and buy dollars to repatriate the money. This puts pressure on the rupee and it loses value against the dollar. The assumption is that at a higher rate of interest the foreign investors might want to invest in Indian bonds and bring in more dollars to do so. This strategy of defending a currency is referred to as the classic interest rate defence and has been practised by both Brazil as well Indonesia in the recent past.
But there are other problems with this approach. Rising interest rates are not good news for economic growth as people are less likely to borrow and spend, when they have to pay higher EMIs. A spate of foreign brokerages have cut their GDP growth forecasts for India for this financial year (i.e. the period between April 1, 2013 and March 31, 2014). Also sectors like banking, auto and real estate are looking even more unattractive in the background of interest rates going up. In fact, auto and banking sectors were anyway down in the dumps.
Slower economic growth could lead to foreign investors selling out of the stock market. When foreign investors sell stocks they get paid in rupees. In order to repatriate this money the foreign investors sell these rupees and buy dollars. And if this situation were to arise, it could put further pressure on the rupee.
Hence by doing what it has done the RBI has put itself in a Catch 22 situation. But then did it really have any other option? The other big question is whether the politicians who actually run the Congress led UPA government will be ready to accept slow economic growth(not that the economy is currently on steroids) so close to the next Lok Sabha elections? On that your guess is as good as mine.
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on July 18, 2013
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek)
The Almighty Dollar and the Fallen Rupee
“I am not an economist. I am an old bond trader,” said Drew Brick, who leads the Market Strategy desk for RBS in the Asia-Pacific region, when Forbes India caught up with him for breakfast on a recent visit to India. “We trade the noise,” he added emphatically.
Right now, the noise is about what US Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke said or didn’t say about his bond-buying. And this is why one needed to know what the “old bond trader” had to say about why the rupee was falling against the dollar. “What is happening now is really not a function of anything really specific to India, although India has an inclination to have problems,” explained Brick. Finance Minister P Chidambaram should welcome at least the first part of his statement, since he has been defending the “fundamentals” of the economy to anybody who would listen.
The foreign exchange market hasn’t been one of them, for it has been cocking a more attentive ear to what Bernanke had to say. And on June 19, he said that the Fed would go slow on its money printing operations in the days to come as the US economy started reviving. “If the incoming data are broadly consistent with this forecast…it would be appropriate to moderate the monthly pace of purchases later this year…And if the subsequent data remain broadly aligned with our current expectations for the economy, we would continue to reduce the pace of purchases in measured steps through the first half of next year, ending purchases around mid-year,” Bernanke said at a press conference that followed the meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
That statement impacted the bond markets most—and the carry trade. The carry trade is about investors who borrow in low-yield currencies to invest in assets in other markets, presumably with higher yields. Bernanke’s statement signalled that bond yields may go up, and that meant carry-trades would have to be unwound. Brick confirmed this: “We are seeing the unwinding of a lot of carry trades that have been taking place across the globe in the chase for yield.”
Brick, who bears a striking resemblance to Hollywood actor Richard Gere, had worked with BNP Paribas, Morgan Stanley and legendary bond kings Pimco before he joined RBS last year. He explained why the dollar is holding up even though US growth isn’t exactly something to write home about. “Some people think that the United States is the least dirty shirt in the drawer. And it has got growth, though not a very high trajectory of growth,” said Brick.
It is this minor revival that is creating problems for carry trade investors who have borrowed and invested money across the world on the assumption that US interest rates will rule close to zero in the foreseeable future.
The return of economic growth in the US has pushed up 10-year treasury bond yields. The yield, which stood at 1.63 percent in the beginning of May, has since risen to 2.5-2.6 percent.
Said Brick: “A bond works by a simple method. It measures three fundamental variables. What are they? Everybody who trades bonds thinks about where is growth going? Where is inflation going? And what is the risk premium?”
And what do we get if we apply this formula to calculate the yield on 10-year US treasuries? Explained Brick: “If the 10-year yield today is around 2.2 percent [it was so, on the day the interview was conducted], what would you say the US nominal growth is? Around 2 percent. What do you think inflation is? Around 1 percent. What do you think the risk premium is in the market place? Clearly it’s risen a little, so maybe it is 30 basis points.” (100 basis points make 1 percent).
This gives us a 3.3 percent yield on 10-year US treasuries. “And when the 10-year treasury is trading at a yield of 2.2 percent, what do you do as a trader? You sell that freakin’ thing. And that’s the risk,” said Brick.
When lots of bonds are sold at the same time, the price of the bond falls and thus the yield, or the return, goes up. And that is precisely what has been happening with 10-year US treasuries, with the yield shooting up by nearly 60 basis points from 1.63 percent in early May to nearly 2.2 percent on June 18, 2013. After Bernanke’s press conference on June 19, the yield shot up dramatically. On June 24, it stood at nearly 2.6 percent.
“The 10-year US treasury is extremely important,” said Brick. This is because it sets the benchmark for interest rates on all other kinds of loans in the United States, from interest rates charged by banks on home loans and home equity loans to interest at which carry trade investors can borrow money. More important for the rupee’s health, when the 10-year US treasury yield goes up, carry trades become less attractive. “The days of quantitative easing-sponsored carry trading are about to be pared, perhaps significantly. Remember, as volume rises, the cost of carry rises and so, too, does market illiquidity,” said Brick.
This is why investors have been selling a lot of the assets they have invested in and repatriating the money back to the United States. The Indian debt market has been hit by this selling and foreign institutional investors (FIIs) have pulled out nearly $5 billion since late May. In fact, stock markets all over the world also fell in the aftermath of Bernanke announcing that he will go slow with his money printing operations in the days to come.
The Federal Reserve has been printing $85 billion every month. It uses $40 billion to buy mortgage-backed securities, and $45 billion to buy long-term American government bonds. By doing so, it has been pumping money into the financial system and keeping interest rates low in order to spur growth.
But the growth did not come. Said Brick: “The truth is that central banks are running up their monetary bases but they are not necessarily getting any bang for the buck in terms of the turnover of the cash that they are creating into the system.”
Bernanke did not say he was going to withdraw all kinds of quantitative easing, or even that he would start withdrawing the easy money. That would require him to sell all the bonds he bought. The market though is getting ready for that to happen. “The market is already trading this. Forward pricing in the markets is already adjusting for this,” said Brick.
Low interest rates in the US after the 2008 Lehman crisis led Asians to borrow a lot in cheap dollars. “All across Asia, non-financial corporations, and even households to a small extent, have been taking out huge amounts of dollar funding,” said Brick. And this may cause some major problems in the days to come. “Right now we are seeing an unwinding of the dollar carry trade but at some point the dollar is going to turn and then the servicing cost of that debt is going to be all the more tricky. Every crisis that I have ever read through, and I am an old man, has always been born on the back of rising rate cycles that move higher with the dollar in tow. This makes the financing cost of debt in emerging markets more expensive. That’s across the board. That’s probably true here in India as well,” he added.
Brick suspects that there are problems lurking in the woodwork. “Corporates are relatively sanguine with a weaker rupee. But where are the cockroaches in the system? Where has the dollar funding been taken on offshore? Have Indians thought about what it means to have a rupee possibly at 65 to a dollar? And what would that possibly mean for the financing cost of banks that have almost certainly been taking on relatively cheap quantitative easing-sponsored cash in their offshore operations to be able to finance lending?”
If the rupee gets to 65 to a dollar, our oil bill will go for a toss. And will gold have a rally in rupee terms, assuming that its price stays stable in dollar terms? “Gold is a zero interest, infinite maturity, inflation-linked bond. That’s all gold is,” Brick responded. The supposed end of quantitative easing in the United States has taken some sheen off the yellow metal. “But it’s possible that we may have another move higher. The selloff has been rather pronounced. But it’s not the core issue here. Gold is a symptom of the larger issue,” said Brick.
Brick also feels that the bond market in the United States might be getting a little ahead of itself.
He reminded us about March 2012, when the 10-year US treasury yield had moved up to 2.4 percent. “Then, Ben Bernanke showed up on the tapes 10 straight trading days, running it back down [i.e. the yield]. My guess is that something like that will occur this time. The market is way ahead of itself.”
The broader point is that if yields rise at a fast pace, they will push up interest rates on loans. This will slow down some of the economic growth that seems to be returning to the United States. And that situation may not be allowed to play out.
So where does that leave Asia? “If quantitative easing gets tapered off as a consequence of relatively strong growth, then quite frankly Asian equities probably will hold in pretty well,” explained Brick.
And then came the but. “But if treasuries sell off massively as a consequence of technical reasons and a marketplace getting well ahead of itself, and dollar funding and interest rates get higher, then equities will get wasted out.”
“What is another scenario? I can give you millions of scenarios. But the truth is we don’t know in the opening stages, the first minutes of a three-hour movie, how it is going to play out. It’s going to be like a Bergman movie. I don’t know how it is going to play out but it is going to be weird at times,” Brick said.
Weird it will be, for “even the end-point of tapering [of Fed bond purchases] leaves the Federal Reserve with a still-gargantuan 25 percent-of-US-GDP balance-sheet. Pressures will sustain, even with reprieves,” Brick concluded.
The interview originally appeared in the Forbes India magazine edition dated July 26, 2013
It's just another manic Monday for the Indian rupee
 Vivek Kaul
Vivek Kaul
The Indian rupee crashed to an all time low level, crossing 61 to a dollar, this morning. As I write this one dollar is worth around Rs 61.2. On Friday when the foreign exchange market closed one dollar was worth Rs 60.24.
The rupee has crashed in response to return on the 10 year American treasury bond spiking to 2.73% on Friday i.e. July 5, 2013. This was an increase of 21 basis points (one basis point is equal to one hundredth of a percentage) in comparison to the return on Wednesday i.e. July 3, 2013. The bond market was closed on July 4, 2013, the American independence day.
A 10 year treasury bond is a bond issued by the American government to finance its fiscal deficit i.e. the difference between what it earns and what it spends. These bonds can be bought and sold in the open market. This buying and selling impacts the price of these bonds and hence their overall return.
The return on the 10 year American treasury bond spiked in response to better than expected jobs data. American businesses added 1,95,000 jobs in June, 2013, which was better than what the market expected. This faster than expected recovery in the job market is being taken as a signal that the American economy is finally getting back on track.
Since the start of the financial crisis in late 2008, the Federal Reserve of United States, the American central bank, has been printing dollars and pumping them into the financial system. This is to ensure that there are enough dollars going around in the financial system, so that interest rates continue to stay low. At low interest rates people are likely to borrow and spend more. Consumer spending makes up for around 71-72% of the American gross domestic product. Hence, an increase in consumer spending is very important for the American economy to keep growing.
The Federal Reserve prints dollars and pumps them into the financial system by buying bonds worth $85 billion every month. This includes government bonds and mortgage backed securities. On June 19,2013, Ben Bernanke, the Chairman of the Federal Reserve of United States, had said that if the American economy kept improving, the Federal Reserve would go slow on money printing in the time to come. He had said that it was possible that the Fed could stop money printing to buy bonds by the middle of next year.
The jobs data has come out better than expected. This is a signal to the bond market that the Federal Reserve will start going slow on money printing sooner rather than later. Several estimates now suggest that the Federal Reserve will start going slow on money printing as soon as September this year.
As and when the Federal Reserve goes slow on money printing the interest rates are likely to go up, as the financial system will have lesser amount of dollars going around. This is likely to push interest rates up. Bond prices are inversely related to interest rates. So as interest rates will go up, bond prices will fall, leading to losses for investors.
But markets don’t wait for things to happen. They start discounting likely happenings in advance.
Given this, the bond market investors are selling out on American government bonds to limit their losses. This has led to bond prices falling. Even when bond prices fall, the interest paid on these bonds continues to remain the same. This means a higher return for the investors who buy the bonds that are being sold.
So this has pushed the return on the 10 year American treasury bond to 2.73%. On May 1, 2013, the return on the 10 year American treasury bond was 1.66%.
An increase in return on government bonds pushes up interest rates on all other loans. This is because lending to the government is deemed to the safest, and hence the return on other loans has to be greater than that, to compensate for the higher risk involved.
As mentioned above, in the aftermath of the financial crisis, the Federal Reserve started to print money, in order to get the American economy up and running again. The trouble was that the average American was just coming out of a huge borrowing binge and was not ready to borrow again, so soon.
But the financial system was slush with money available at very low interest rates. This led to large institutional investors indulging in what came to be known as the dollar carry trade. Money was borrowed in dollars at low interest rates and invested in financial assets all over the world. The difference in return between what the investor makes and the interest he pays on his dollar borrowing, is referred to as the carry.
With interest rates in the United States going up, as returns on government bonds up, the carry made on the dollar carry trade has been on its way down. The arbitrage that investors were indulging in by borrowing in dollars and investing those dollars all across the world with a prospect of making higher returns is no longer as viable as it used to be.
A lot of this money came into the Indian stock market as well as the bond market. In case of the bond market the amount of return that can made is limited. Hence, carry trade investors who had invested in Indian bonds have been selling out. Between May end and now, foreign investors have sold out around $6 billion worth of Indian bonds.
When they sell out on these bonds, the investors are paid in rupees. In order to repatriate these rupees abroad they need to convert them into dollars. Hence they sell rupees to buy dollars. When they sell rupees there is a surfeit of rupees in the market and not enough dollars going around. In this scenario, the rupee tends to fall in value against the dollar.
And that’s what has happened in the morning today when the rupee crossed 61 to a dollar. As the rupee loses value against the dollar, foreign investors face a higher amount of currency risk, leading to more of them selling out. This puts further pressure on the rupee. ( you can read more about it here).
The pressure on the rupee will continue in the days to come. If American bond yields keep going up, more foreign investors will sell out of India and this will lead to the rupee continuing to lose value against the dollar. Over and above that there are several home grown issues that will ensure that the rupee will keep depreciating against the dollar. (You can read more about it here) This is not the last manic Monday we have seen as far as the rupee is concerned.
PS: In the time that it took me to write this piece, the rupee recovered against the dollar. One dollar is now worth around Rs 60.99. Looks like the RBI has intervened to sell dollars and buy rupees.
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on July 8,2013.
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek)
When it comes to the rupee, ‘you ain’t seen nothin’ yet’
 Vivek Kaul
Vivek Kaul
The Reserve Bank of India(RBI) painted a very worrying picture of India’s external debt scenario in a report released late last week. The total external debt of the country stood at US$ 390 billion as on March 31,2013. This was an increase of US$ 44.6 billion or 12.9 per cent in comparison to March 31, 2012.
Even on a quarterly basis the increase is substantial. As on December 31, 2012, the total external debt had stood at $376.3 billion. This implies an increase of 3.6% of the three month period between December, 2012 and March, 2013.
The external debt typically consists of external commercial borrowings (ECBs) raised by companies, NRI deposits, loans raised from the IMF and other countries, short term trade credit etc. What is worrying here is that nearly 44.2% or $172.4 billion of the outstanding external debt matures on or before March 31, 2014.
The borrower will have to sell rupees and buy dollars in order to repay this maturing foreign debt. When this happens, it might lead to a surfeit of rupees and a shortage of dollars in the foreign exchange market, leading to a further fall in value of the rupee against the dollar.
The foreign investors pulled out investments worth more than Rs 44,000 crore from the Indian debt and equity markets during the month of June, 2013. During the process of conversion of these rupees into $7.53 billion, the demand for dollars went up, and pushed the value of one dollar beyond sixty rupees. The rupee has since recovered a little, and as I write this one dollar is worth around Rs 59.24.
The broader point is that if the demand for $7.53 billion can cause a massacre of the Indian rupee against the dollar, $172.4 billion of debt which needs to be repaid before March 31, 2014, can create a bigger havoc.
The ratio of debt that needs to be paid before March 31, 2014, to the foreign exchange reserves of India is around 59%. This was at 17% as on March 31, 2008. This is another number that tells us very clearly the precarious position India is in as far as its external debt is concerned.
One factor that needs to be considered here is that all the maturing debt may not need to be repaid. Take the case of NRI deposits. As on March 31, 2013, they stood at around $70.8 billion, having gone up nearly 20.8% since March 31, 2012. NRIs typically invest in India because the interest that they earn on deposits is higher in comparison to what they would earn by investing in the countries that they live in.
Interest rates offered on bank deposits continue to remain high in India in comparison to the western countries. So does that mean that NRIs will renew their deposits and not take their money out of India?
Interest is not the only thing NRIs need to consider while investing money in India. They also need to take currency risk into account. With the rupee depreciating against the dollar, the ‘perception’ of currency risk has gone up. Lets understand this through an example.
An NRI invests $10,000 in India. At the point he gets money into India $1 is worth Rs 55. So $10,000 when converted into rupees, amounts to Rs 5.5 lakh. This money lets assume is invested at an interest rate of 10%. A year later Rs 5.5 lakh has grown to Rs 6.05 lakh (Rs 5.5 lakh + 10% interest on Rs 5.5 lakh). The NRI now has to repatriate this money back. At this point of time lets say $1 is worth Rs 60. So when the NRI converts rupees into dollars he gets $10,080 or more or less the same amount of money that he had invested.
With the rupee depreciating against the dollar, the ‘perception’ of currency risk has thus gone up. Given this, NRIs are more likely to repatriate their maturing deposits, rather than renew them, and this will put pressure on the rupee dollar exchange rate. Data from the RBI suggests that NRI deposits worth nearly $49 billion mature on or before March 31, 2014.
External commercial borrowings worth $21 billion need to be repaid before March 31, 2014. Companies can pay off these loans by raising fresh loans. But in the aftermath of the Federal Reserve of United States, the American central bank, deciding to “taper” or go slow on the money printing, fresh loans may not be so easy to come by. Also, businesses may want to pay up as quickly as possible given that more the rupee depreciates against the dollar, the greater is the amount in rupees they would need to buy dollars needed to repay there loans.
Interestingly, nearly $43.3 billion of external commercial borrowings are set to mature between April 1, 2014 and March 31, 2016.
So to cut a long story shot, much of the external debt maturing before March 31, 2014 will have to repaid and this will put further pressure on the rupee vis a vis the dollar.
India’s burgeoning external debt is only a recent phenomenon. As on March 31, 2007, the total external debt had stood at $169.7 billion. Since then it has jumped by a massive 129.8% to $390 billion. There are basically two reasons for the same.
The first reason is the burgeoning fiscal deficit of the Congress led United Progressive Alliance(UPA) government. Fiscal deficit is the difference between what a government earns and what it spends. For 2007-2008(i.e. the period between April 1, 2007 and March 31, 2008), the fiscal deficit had stood at Rs 1,26,912 crore. For the year 2013-2014 (i.e. the period between April 1, 2013 and March 31, 2014) it is projected to be at Rs 5,42,599 crore or nearly 327.5% higher.
The higher fiscal deficit has been financed through greater borrowings made by the government. In order to borrow money the government had to offer better terms than available elsewhere, and thus managed to push up interest rates. This encouraged NRIs to invest their money in India. NRI deposits have increased from $41.24 billion as on March 31, 2007, to $70.82 billion as on March 31, 2013.
Higher interest rates also led to businesses looking at cheaper options abroad. External commercial borrowings went up from $41.44 billion as on March 31, 2007 to $120.89 billion as on March 31, 2013. Interest rates were lower abroad primarily because the Western central banks had unleashed a huge money printing effort in the aftermath of the financial crisis that started in late 2008 to get their respective economies up and running again. And this is the second reason behind India’s burgeoning foreign debt.
To conclude, tough times lie ahead for the rupee. The recent Financial Stability Report released by the RBI points out that “rise in India’s overall external debt is an added source of concern.” But that is a very mild “British” sort of way of putting it. What we need here is a classic American expression. When it comes to the rupee “you ain’t seen nothin’ yet”.
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on July 1, 2013
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek)
