 Vivek Kaul
Vivek Kaul
The Reserve Bank of India(RBI) is doing everything that it can do to stop the rupee from falling against the dollar. Yesterday it announced further measures on that front.
Each bank will now be allowed to borrow only upto 0.5% of its deposits from the RBI at the repo rate. Repo rate is the interest rate at which RBI lends to banks in the short term and it currently stands at 7.25%.
Sometime back the RBI had put an overall limit of Rs 75,000 crore, on the amount of money that banks could borrow from it, at the repo rate. This facility of banks borrowing from the RBI at the repo rate is referred to as the liquidity adjustment facility.
The limit of Rs 75,000 crore worked out to around 1% of total deposits of all banks. Now the borrowing limit has been set at an individual bank level. And each bank cannot borrow more than 0.5% of its deposits from the RBI at the repo rate. This move by the RBI is expected bring down the total quantum of funds available to all banks to Rs 37,000 crore, reports The Economic Times.
In another move the RBI tweaked the amount of money that banks need to maintain as a cash reserve ratio(CRR) on a daily basis. Banks currently need to maintain a CRR of 4% i.e. for every Rs 100 of deposits that the banks have, Rs 4 needs to set aside with the RBI.
Currently the banks need to maintain an average CRR of 4% over a reporting fortnight. On a daily basis this number may vary and can even dip under 4% on some days. So the banks need not maintain a CRR of Rs 4 with the RBI for every Rs 100 of deposits they have, on every day.
They are allowed to maintain a CRR of as low as Rs 2.80 (i.e. 70% of 4%) for every Rs 100 of deposits they have. Of course, this means that on other days, the banks will have to maintain a higher CRR, so as to average 4% over the reporting fortnight.
This gives the banks some amount of flexibility. Money put aside to maintain the CRR does not earn any interest. Hence, if on any given day if the bank is short of funds, it can always run down its CRR instead of borrowing money.
But the RBI has now taken away that flexibility. Effective from July 27, 2013, banks will be required to maintain a minimum daily CRR balance of 99 per cent of the requirement. This means that on any given day the banks need to maintain a CRR of Rs 3.96 (99% of 4%) for every Rs 100 of deposits they have. This number could have earlier fallen to Rs 2.80 for every Rs 100 of deposits. The Economic Times reports that this move is expected to suck out Rs 90,000 crore from the financial system.
With so much money being sucked out of the financial system the idea is to make rupee scarce and hence help increase its value against the dollar. As I write this the rupee is worth 59.24 to a dollar. It had closed at 59.76 to a dollar yesterday. So RBI’s moves have had some impact in the short term, or the chances are that the rupee might have crossed 60 to a dollar again today.
But there are side effects to this as well. Banks can now borrow only a limited amount of money from the RBI under the liquidity adjustment facility at the repo rate of 7.25%. If they have to borrow money beyond that they need to borrow it at the marginal standing facility rate which is at 10.25%. This is three hundred basis points(one basis point is equal to one hundredth of a percentage) higher than the repo rate at 10.25%. Given that, the banks can borrow only a limited amount of money from the RBI at the repo rate. Hence, the marginal standing facility rate has effectively become the repo rate.
As Pratip Chaudhuri, chairman of State Bank of India told Business Standard “Effectively, the repo rate becomes the marginal standing facility rate, and we have to adjust to this new rate regime. The steps show the central bank wants to stabilise the rupee.”
All this suggests an environment of “tight liquidity” in the Indian financial system. What this also means is that instead of borrowing from the RBI at a significantly higher 10.25%, the banks may sell out on the government bonds they have invested in, whenever they need hard cash.
When many banks and financial institutions sell bonds at the same time, bond prices fall. When bond prices fall, the return or yield, for those who bought the bonds at lower prices, goes up. This is because the amount of interest that is paid on these bonds by the government continues to be the same.
And that is precisely what happened today. The return on the 10 year Indian government bond has risen by a whopping 33 basis points to 8.5%. Returns on other bonds have also jumped.
Debt mutual funds which invest in various kinds of bonds have been severely impacted by the recent moves of the RBI. Since bond prices have fallen, debt mutual funds which invest in these bonds have faced significant losses.
In fact, the data for the kind of losses that debt mutual funds will face today, will only become available by late evening. But their performance has been disastrous over the last one month. And things should be no different today.
Many debt funds have lost as much as 5% over the last one month. And these are funds which give investors a return of 8-10% over a period of one year. So RBI has effectively killed the debt fund investors in India.
But then there was nothing else that it could really do. The RBI has been trying to manage one side of the rupee dollar equation. It has been trying to make rupee scarce by sucking it out of the financial system.
The other thing that it could possibly do is to sell dollars and buy rupees. This will lead to there being enough dollars in the market and thus the rupee will not lose value against the dollar. The trouble is that the RBI has only so many dollars and it cannot create them out of thin air (which it can do with rupees). As the following graph tells us very clearly, India does not have enough foreign exchange reserves in comparison to its imports.
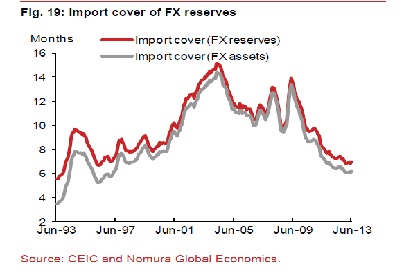
The ratio of foreign exchange reserves divided by imports is a little over six. What this means is that India’s total foreign exchange reserves as of now are good enough to pay for imports of around a little over six months. This is a precarious situation to be in and was only last seen in the 1990s, as is clear from the graph.
The government may be clamping down on gold imports but there are other imports it really doesn’t have much control on. “The commodity intensity of imports is high,” write analysts of Nomura Financial Advisory and Securities in a report titled India: Turbulent Times Ahead. This is because India imports a lot of coal, oil, gas, fertilizer and edible oil. And there is no way that the government can clamp down on the import of these commodities, which are an everyday necessity. Given this, India will continue to need a lot of dollars to import these commodities.
Hence, RBI is not in a situation to sell dollars to control the value of the rupee. So, it has had to resort to taking steps that make the rupee scarce in the financial system.
The trouble is that this has severe negative repercussions on other fronts. Debt fund investors are now reeling under heavy losses. Also, the return on the 10 year bonds has gone up. This means that other borrowers will have to pay higher interest on their loans. Lending to the government is deemed to be the safest form of lending. Given this, returns on other loans need to be higher than the return on lending to the government, to compensate for the greater amount of risk. And this means higher interest rates.
The finance minister P Chidambaram has been calling for lower interest rates to revive economic growth. But he is not going to get them any time soon. The mess is getting messier.
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on July 24, 2013
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek)
marginal standing facility rate
Why RBI is in a Catch 22 situation when it comes to the rupee
 Vivek Kaul
Vivek Kaul
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will carry out an open market operation and sell government of India bonds worth Rs 12,000 crore today i.e. July 18,2013.
The RBI carries out an open market operation in order to suck out or put in rupees into the financial system. When the RBI needs to suck out rupees from the system it sells government of India bonds, like it is doing today.
Banks and other financial institutions buy these bonds and pay the RBI in rupees, and thus the RBI sucks out rupees from the market.
The rupee has had a tough time against the US dollar lately and had recently touched an all time low of 61.23 to a dollar. By selling bonds, the RBI wants to suck out rupees from the financial system and thus try and ensure that rupee gains value against the dollar.
The RBI has been trying to defend the value of the rupee against the dollar by selling dollars from the foreign exchange reserves that it has. When the RBI sells dollars it leads to a surfeit of dollars in the market and as a result the dollar loses value against the rupee or at least the rupee does not fall as fast as it otherwise would have.
The trouble is that the RBI does not have an unlimited supply of dollars. Unlike the Federal Reserve of United States, the RBI cannot create dollars out of thin air by printing them. In the period of three weeks ending July 5, 2013, as the RBI sold dollars to defend the rupee, the foreign exchange reserves fell by $10.5 billion to $280.17 billion.
At this level India has foreign exchange reserves that are enough to cover around 6.3 months worth of imports. Such low levels of foreign exchange expressed as import cover hasn’t been seen since the early 1990s. Given this, there isn’t much scope for the RBI to sell dollars and hope to control the value of the rupee. It simply doesn’t have enough dollars going around.
Hence, it is trying to control the other end of the equation. It cannot ensure that there are enough dollars going around in the market, so its trying to create a shortage of rupees, by selling government of India bonds.
In fact, as a part of this plan the RBI has also put an overall limit of Rs 75,000 crore, on the amount of money banks can borrow from it, at the repo rate of 7.25%. Repo rate is the interest rate at which RBI lends money to banks in the short term.
Banks can borrow money beyond this limit at what is known as the marginal standing facility rate. This rate has been raised by 200 basis points(one basis point is one hundredth of a percentage) to 10.25%. Hence, borrowing from the RBI has been made more expensive.
A major motive behind this move was to rein in the speculators. As Jehangir Aziz of JP Morgan Chase wrote in The Indian Express “It has been ridiculously cheap over the last month to borrow rupees at the overnight rate, buy dollars and then wait for the exchange rate to crumble. In June, the monthly overnight interest rate was 0.5 per cent and the depreciation 10 per cent.”
Lets understand this through an example. Lets say a speculator borrows Rs 54,000 at a monthly interest rate of 0.5%. This is at a point of time when one dollar is worth Rs 54. He uses this money to buy dollars and ends up buying $1000 (Rs 54,000/54). When he sells rupees to buy dollars it puts pressure on the value of the rupee against the dollar.
After buying dollars, the speculator just sits on it for a month, by the time rupee has depreciated 10% against the dollar and one dollar is worth Rs 59.4(Rs 54 + 10% of Rs 54). He sells the dollars, and gets Rs 59,400($1000 x 60) in return. He needs to repay Rs 54,000 plus a 0.5% interest on it. The rest is profit. This is how speculators had been making money for sometime and thus putting pressure on the rupee.
By making it more expensive to borrow, the RBI hopes to control the speculation and thus ensure that there is lesser pressure on the rupee.
The message that the market seems to have taken from the efforts of the RBI to create a scarcity of rupees is that interest rates are on their way up. The hope is that at higher interest rates foreign investors will bring in more dollars and convert them into rupees and buy Indian bonds. Foreign investors have sold off bonds worth $8.4 billion since their peak so far this year.
When foreign investors sell bonds they get paid in rupees. They sell these rupees and buy dollars to repatriate the money. This puts pressure on the rupee and it loses value against the dollar. The assumption is that at a higher rate of interest the foreign investors might want to invest in Indian bonds and bring in more dollars to do so. This strategy of defending a currency is referred to as the classic interest rate defence and has been practised by both Brazil as well Indonesia in the recent past.
But there are other problems with this approach. Rising interest rates are not good news for economic growth as people are less likely to borrow and spend, when they have to pay higher EMIs. A spate of foreign brokerages have cut their GDP growth forecasts for India for this financial year (i.e. the period between April 1, 2013 and March 31, 2014). Also sectors like banking, auto and real estate are looking even more unattractive in the background of interest rates going up. In fact, auto and banking sectors were anyway down in the dumps.
Slower economic growth could lead to foreign investors selling out of the stock market. When foreign investors sell stocks they get paid in rupees. In order to repatriate this money the foreign investors sell these rupees and buy dollars. And if this situation were to arise, it could put further pressure on the rupee.
Hence by doing what it has done the RBI has put itself in a Catch 22 situation. But then did it really have any other option? The other big question is whether the politicians who actually run the Congress led UPA government will be ready to accept slow economic growth(not that the economy is currently on steroids) so close to the next Lok Sabha elections? On that your guess is as good as mine.
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on July 18, 2013
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek)