Vivek Kaul
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), America’s premier stock market index, has been quoting at all-time-high levels. On 7 March 2013, it closed at 14,329.49 points. This has happened in an environment where the American economy and corporate profitability has been down in the dumps.
The Indian stock markets too are less than 10 percent away from their all-time peaks even though the economy will barely grow at 5 percent this year.
All the easy money created by the Federal Reserve is landing up in the stock market. So the stock market is going up because there is too much money chasing stocks. ReutersIn this scenario, should one dump stocks or buy them?
The short answer is simple: as long as the other markets are doing fine, we will do fine too. The Indian market’s performance is more closely linked to the fortunes of other stock markets than to Indian economic performance.
So watch the world and then invest in the Sensex or Nifty. You can’t normally go wrong on this.
Let’s see how the connection between the real economy and the stock market has broken down after the Lehman crisis.
The accompanying chart below proves a part of the point I am trying to make. It tells us that the total liabilities of the American government are huge and currently stand at 541 percent of GDP. The American GDP is around $15 trillion. Hence the total liability of the American government comes to around $81 trillion (541 percent of $15 trillion).

Source: Global Strategy Weekly, Cross Asset Research, Societe Generate, March 7, 2013
The total liability of any government includes not only the debt that it currently owes to others but also amounts that it will have to pay out in the days to come and is currently not budgeting for.
Allow me to explain. As economist Laurence Kotlikoff wrote in a column in July last year, “The 78 million-strong baby boom generation is starting to retire in droves. On average, each retiring boomer can expect to receive roughly $35,000, adjusted for inflation, in Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid benefits. Multiply $35,000 by 78 million pairs of outstretched hands and you get close to $3 trillion per year in costs.”
The $3trillion per year that the American government needs to pay its citizens in the years to come will not come out of thin air. In order to pay out that money, the government needs to start investing that money now. And that is not happening. Hence, this potential liability in the years to come is said to be unfunded. But it’s a liability nonetheless. It is an amount that the American government will owe to its citizens. Hence, it needs to be included while calculating the overall liability of the American government.
So the total liabilities of the American government come to around $81 trillion. The annual world GDP is around $60 trillion. This should give you, dear reader, some sense of the enormity of the number that we are talking about.
And that’s just one part of the American economic story. In the three months ending December 2012, the American GDP shrank by 0.1 percent. The “U3” measure of unemployment in January 2013 stood at 7.9 percent of the labour force. There are various ways in which the Bureau of Labour Standards in the United States measures unemployment. This ranges from U1 to U6. The official rate of unemployment is the U3, which is the proportion of the civilian labour force that is unemployed but actively seeking employment.
U6 is the broadest definition of unemployment and includes workers who want to work full-time but are working part-time because there are no full-time jobs available. It also includes “discouraged workers”, or people who have stopped looking for work because economic conditions make them believe that no work is available for them. This number for January, 2013, stood at 14.4 percent.
The business conditions are also deteriorating. As Michael Lombardi of Profit Confidential recently wrote, “As for business conditions, they appear bright only if you look at the stock market. In reality, they are deteriorating in the US economy. For the first quarter of 2013, the expectations of corporate earnings of companies in the S&P 500 have turned negative. Corporate earnings were negative in the third quarter of 2012, too.”
The average American consumer is not doing well either. “Consumer spending, hands down the biggest contributor of economic growth in the US economy, looks to be tumbling. In January, the disposable income of households in the US economy, after taking into consideration inflation and taxes, dropped four percent—the biggest single-month drop in 20 years!,” writes Lombardi.
Consumption makes up for nearly 70 percent of the American GDP. And when the American consumer is in the mess that he is where is the question of economic growth returning?
So why is the stock market rallying then? A stock market ultimately needs to reflect the prevailing business and economic conditions, which is clearly not the case currently.
The answer lies in all the money that is being printed by the Federal Reserve of the United States, the American central bank. Currently, the Federal Reserve prints $85 billion every month, in a bid to keep long-term interest rates on hold and get the American consumer to borrow again. The size of its balance-sheet has touched nearly $3 trillion. It was at around $800 billion at the start of the financial crisis in September 2008.
As Lombardi puts it, “When trillions of dollars in paper money are created out of thin air and interest rates are simultaneously reduced to zero, where else would investors put their money?”
All the easy money created by the Federal Reserve is landing up in the stock market.
So the stock market is going up because there is too much money chasing stocks. The broader point is that the stock markets have little to do with the overall state of economy and business.
This is something that Aswath Damodaran, valuation guru, and professor at the Columbia University in New York, seemed to agree with, when I asked him in a recent interview about how strong is the link between economic growth and stock markets? “It is getting weaker and weaker every year,” he had replied.
This holds even in the context of the stock market in India. The economy which was growing at more than 8 percent per year is now barely growing at 5 percent per year. Inflation is high at 10 percent. Borrowing rates are higher than that. When it comes to fiscal deficit we are placed 148 out of the 150 emerging markets in the world. This means only two countries have a higher fiscal deficit as a percentage of their GDP, in comparison to India. Our inflation rank is around 118-119 out of the 150 emerging markets.
More and more Indian corporates are investing abroad rather than in India (Source: This discussion featuring Morgan Stanley’s Ruchir Sharma and the Chief Economic Advisor to the government Raghuram Rajan on NDTV). But despite all these negatives, the BSE Sensex, India’s premier stock market index, is only a few percentage points away from its all-time high level.
Sharma, Managing Director and head of the Emerging Markets Equity team at Morgan Stanley Investment Management, had a very interesting point to make. He used thefollowing slide to show how closely the Indian stock market was related to the other emerging markets of the world.

India’s premier stock market index, is only a few percentage points away from its all-time high level.
As he put it, “It has a correlation of more than 0.9. It is the most highly correlated stock market in the entire world with the emerging market averages.”
So we might like to think that we are different but we are not. “We love to make local noises about how will the market react pre-budget/post-budget and so on, but the big picture is this. What drives a stock market in the short term, medium term and long term is how the other stock markets are doing,” said Sharma. So if the other stock markets are going up, so does the stock market in India and vice versa.
In fact, one can even broaden the argument here. The state of the American stock market also has a huge impact on how the other stock markets around the world perform. So as long as the Federal Reserve keeps printing money, the Dow will keep doing well. And this in turn will have a positive impact on other markets around the world.
To conclude let me quote Lombardi of Profit Confidential again “I believe the longer the Federal Reserve continues with its quantitative easing and easy monetary policy, the bigger the eventual problem is going to be. Consider this: what happens to the Dow Jones Industrial Average when the Fed stops printing paper money, stops purchasing US bonds, and starts to raise interest rates? The opposite of a rising stock market is what happens.”
But the moral is this: when the world booms, India too booms. Keep your fingers crossed if the boom is lowered some time in the future.
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on March 8, 2013.
Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek
Inflation
Dear PM, those who live in glass houses don't throw stones at others

The nation came to the realisation yesterday that the Prime Minister Manmohan Singh actually has a voice. And then we all came to the conclusion that just because he decided to speak, he spoke well. One commentator even went onto christen the event as “Manmohan on steroids”.
The part that the media loved the most was when Singh told the Parliament ‘Jo garajte hain, woh baraste nahi(Thunderous clouds do not bring showers)’, a clichéd statement which was supposed to put the Bhartiya Janata Party (BJP), the main opposition party, in its place.
As far as clichés go, I would take this opportunity, to bring to your notice, dear readers, a dialogue written by Akhtar-Ul-Iman and delivered with great panache by Raj Kumar in the Yash Chopra directed Waqt. The line goes like this: “Chinoi Seth…jinke apne ghar sheeshe ke hon, wo dusron par pathar nahi feka karte (Chinoi Seth…those who live in glass houses don’t throw stones at others).”
Now Singh may not have time to sit through a movie which runs into 206 minutes, given that he is the Prime Minister of the nation, and probably has decisions to make and things to do. But he would be well-advised to watch this 18-second YouTube clip and hopefully come to the realisation that those who live in glass houses, like Singh and his government, do not throw stones at others.
In fact, Singh’s speech to the Parliament yesterday was riddled with many inconsistent and wrong claims. It is a real surprise that the BJP has not caught onto rubbishing the arguments presented by Singh. Let us examine a few claims made by Singh:
Even BIMARU states have also done much better in UPA period than previous period: BIMARU is an acronym used for the states of Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. These are states which have lagged in economic growth for a long period of time. There has been a recent spurt in their economic growth and this claims Singh has been because of the UPA government.
Three out of the four states (except Rajasthan) have had a non Congress-non UPA government for the entire duration of the UPA rule in Delhi. Rajasthan has had a Congress government since December 2008.
So trying to claim that the growth in these states has been only because of the UPA government is misleading to say the least. The argument is along similar lines where Congress politicians and some experts have tried to claim over and over again that Bihar has grown faster than Gujarat. Yes it has in percentage terms. But what they forget to tell us is that Gujarat is growing on a much higher base, meaning the absolute growth in Gujarat is higher. In fact, it is three times higher than that of Bihar (The entire argument is explained here).
If we look at the MSP across various commodities, they have increased by 50 to 200% since 2004-05: The government offers a minimum support price on various commodities including rice and wheat. At this price, the Food Corporation of India (FCI), or a state agency acting on its behalf, purchase primarily rice and wheat, grown by Indian farmers. The theory behind setting the MSP is that the farmer will have some idea the price he would get when he sells his produce after harvest. What it has led to is that more and more farmers are selling to the government because they have an assured buyer at an assured price. The government now has nearly Rs 60,000 crore of rice and wheat in excess of what it needs to maintain a buffer stock. While the government is hoarding onto more rice and wheat than it needs, there is a shortage of wheat and rice in the open market pushing up their prices and in turn food inflation and consumer price inflation. It has also pushed up food subsidies and fiscal deficit. Fiscal deficit is the difference between what the government earns and what it spends. And if the government continues with this policy there are likely to be other negative consequences as well. (The entire argument is explained here)
The current slowdown in industrial growth is a concern: This was the most tepid statement in the entire speech. Is it just a concern? Some of the biggest Indian industrialists have gone on record to say that they would rather invest abroad than in India. As Kumar Manglam Birla recently said in an interview “Country risk for India just now is pretty elevated and chances are that for deployment of capital, you would look to see if there is an asset overseas rather than in India…We are in 36 countries around the world. We haven’t seen such uncertainty and lack of transparency in policy anywhere.” The Birlas have known to be very close to the Congress party for a very long time.
And numbers bear this story. Indian corporates are investing abroad rather than India. In 2001-2002 this number was less than 1% of the gross domestic product (GDP) and currently it stands at 6% of the GDP (Source: This discussion featuring Morgan Stanley’s Ruchir Sharma and the Chief Economic Advisor to the government Raghuram Rajan on the news channel NDTV). So the situation is clearly more than just a concern. If Indian industrialists don’t want to invest in India who else will? Is it time to say good bye to industrial growth? Maybe the Prime Minister has an answer for that.
The economic growth has slowed down in 2012-13, because of the difficult global situation: This is something which the finance minister P Chidambaram also alluded to in his budget speech. What it tells us is that there is very little acknowledgement of mistakes that have been made by this government led by Manmohan Singh over the years.
When India was growing at growth rates of 8% and greater, there was a lot of chest thumping by various constituents of the government, that look we are growing at such a high rate. Now that we are not growing at the same speed its because of a difficult global situation.
Ruchir Sharma in a post budget discussion on the news channel NDTV made a very interesting point. India has consistently been at around 24-26th position among 150 emerging market countries when it comes to economic growth over the last three decades.
We thought we were growing at a very fast rate over the last few years, but so was everyone else. As Sharma put it “The last decade we thought we had moved to a higher normal and it was all about us. Every single emerging market in the world boomed and the rising tide lifted all boats including us.”
But now that we are not growing as fast as we were it is because the global economy has slowed down. Sharma nicely summarised this disconnect when he said “When the downturn happens it is about the global economy. When we do well its about us.” India currently has fallen to the 40th position when it comes to economic growth.
Will bring the country back to 8% growth rate: This is kite flying of the worst kind. As Sharma of Morgan Stanley told NDTV “I see people in government today including the Prime Minister talking about 8% GDP growth rate as if that is the level we should be. There is nothing to suggest that is our potential.”
Singh said that the government was committed to achieving a 8% growth rate for the period of the 12th five year plan period of 2012-2017. In the first year of this plan i.e. the financial year 2012-2013 (the period between April 1, 2012 and March 31, 2013), the Indian economy is expected to grow at around 5%(numbers projected by the Central Statistical Organisation).
What that means is that if the 8% target is to be achieved, the economy has to consistently grow at 9% per year for the remaining four years of the plan. And India has never experienced such consistent high growth ever in the past.
Given that Singh’s statement needs to be taken with a pinch of salt. It is essentially rhetoric of the worst kind. As Nate Silver writes in The Signal and the Noise “Sometimes economic forecasts have expressively political purposes too. It turns out that economic forecasts produced by the White House , for instance, have historically been among the least accurate of all, regardless of whether it’s a Democrat or Republican in charge. When it comes to economic forecasting, however, the stakes are higher than for political punditry. As Robert Lucas pointed out, the line between economic forecasting and economic policy is very blurry: a bad forecast can make the real economy worse.” Singh’s 8% growth statement needs to be viewed along similar lines.
There were many things that Singh did not talk about. Among 150 emerging markets, the fiscal deficit of the Indian government is currently at the 148th number. When it comes to inflation, India is currently at the 118-119th position. The current account deficit (which Singh did talk about) will touch an all time high during the course of the financial year 2012-2013. Interest rates have stubbornly refused to come down. And so on.
To conclude, Manmohan Singh was in poetic mood yesterday. “Humko hai unse wafa ki umeed, jo nahi jaante wafa kya hai (We hope for loyalty from those who do not know the meaning of the word),” the prime minister said quoting the Urdu poet Mirza Ghalib, while taking pot-shots at the BJP.
It’s time the BJP got back to him with what are the most famous lines of the poet Akbar Allahabadi.
“Hum aah bhi karte hain to ho jaate hain badnam,
wo qatl bhi karte hain to charcha nahi hota.”
(badnam = infamous. Qatl = murder. Charcha = discussion)
This article originally appeared on www.firstpsost.com on March 7, 2013, with a different headline.
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek)
UPA-nomics: How to hoard grain and let food prices soar
Vivek Kaul
Over the last few days my mother and her sister have been complaining about how the price of the 10 kg bag of rice that they buy has gone up by 17% in just over a couple of month’s time.
Now contrast this with what Akhilesh Tilotia of Kotak Institutional Equities Research writes in the GameChanger Perspectives report titled Putting the mountain of grains to use (Released on March 5, 2013). “India can raise more than Rs60,000 crore if it prunes its inventory of food grains: an excess 20 million tons of rice and 26 million tons of wheat (without accounting for procurements to be made this year),” writes Tilotia. (The table shows the numbers in detail).
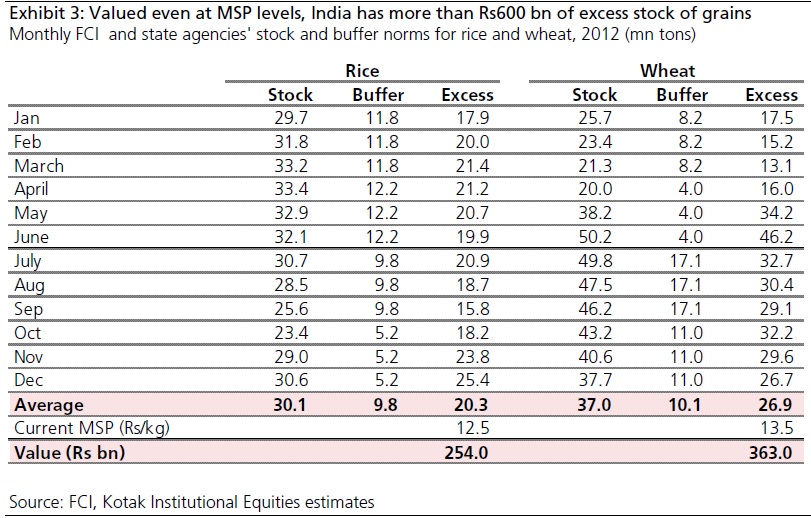
As the above table shows the government currently has an excess rice stock worth around Rs 25,400 crore and an excess wheat stock worth Rs 36,300 crore, or more than Rs 60,000 crore in total. These numbers have been arrived at by taking into account the MSP of rice at Rs 12.5 per kg and the MSP of wheat at Rs 13.5 per kg and multiplying them with the excess stocks. What the table also tells us is that the government currently has an excess rice stock of nearly 2 times the buffer and an excess wheat stock of nearly 2.7 times the buffer.
The government sets a minimum support price(MSP) for wheat and rice. Every year the Food Corporation of India (FCI), or a state agency acting on its behalf, purchases rice and wheat at MSPs set by the government. The “supposed” idea behind setting the MSP much and that too much in advance is to give the farmer some idea of how much he should expect to earn when he sells his produce a few months later. FCI typically purchases around 15-20 percent of India’s wheat output and 12-15 percent of its rice output, estimates suggest.
At least this is how things are supposed to work in theory. But most government motives have unintended consequences. With an assured price more rice and wheat lands up with the government than it distributes through the public distribution system. Also with FCI obligated to purchase what the farmers bring in, its godowns overflow and at times the wheat and rice are dumped in the open, leading to rodents feasting on the crop.
On the other hand the way things currently are it helps the farmer as he has an assured buyer in the government for his produce. But what it also does is it pushes up prices of rice and wheat everywhere else, as more of it lands up in the godowns of FCI and not in the open market.
The procurement also adds to the food subsidy. The government pays for all the rice and wheat that the farmer brings to it and then lets a lot of it rot. The government currently has nearly 67 million tonnes of rice and wheat in stock. Of this nearly 47 million tonnes is excess.
Tilotia expects the rice and wheat stock of the government to go up to 100 million tonnes by the time this harvest season gets over. As he writes “After the current harvest season, Indian granaries will stock about 100 million tonnes of wheat and rice…A high inventory comes with a heavy carrying cost, which the FCI estimates at Rs6.12 per kg for year-end September 2014: At 100 million tons, this will cost India Rs 60,000 crore a year (forming most of its food subsidy bill).”
A higher food subsidy bill adds to the fiscal deficit and which as writers Firstpost regularly keeps discussing has huge consequences of its own. Fiscal deficit is the difference between what a government spends and what it earns.
In fact, the United States of America had a similar policy in place in the aftermath of The Great Depression which started in 1929, on a number of agri-commodities like wheat, tobacco, cotton etc. The government offered a support price to farmers. This support price had unintended consequences over the years, especially in case of wheat.
As Bruce Gardner writes in the research paper “The Political Economy of U.S.Export Subsidies for Wheat” (quoted by Tilotia) “The traditional means of price support is a governmental agreement, through its Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC), to buy wheat at the support price. This programme periodically led to governmental acquisition of large stocks which were costly to store and for which markets did not exist at the support price level.”
As is happening in India right now the American government ended up buying more and more wheat, of which it had no use for, especially at the price it was paying for it. The farmers had an assured buyer in the government and they went around producing more wheat than before.
This resulted in excess stocks with the American government. Over the years this excess wheat was exported at a subsidised rates. As Gardner writes “The subsidy ranged from 5 to 30 percent of the price of wheat, depending on world and U.S. market conditions in each year.” A lot of wheat was also donated under the Agricultural Trade and Development Act of 1954 ( better known as P.L. 480) of which India was a huge beneficiary in the late 50s and early 60s till Lal Bahadur Shastri initiated the agricultural revolution.
Gradually the wheat acreage, or the area over which wheat was planted, was also reduced in the United States. This meant that the farmers had to keep their land idle and not plant wheat on it. “Acreage allotments…were reintroduced in 1954 and reduced planted acreage by about 18 million acres (from 79 million in 1953 to an average of 61 million in 1954-56). Each producer had to stay under the farm’s allotment in order to be eligible for price support loans. In 1956 the Soil Bank program was introduced. It paid wheat growers about $20 per acre (roughly market rental rates) to idle an average of 12 million more acres (20 percent of preprogram acreage) in 1956-58,” writes Gardner.
India seems to be heading on the same path if the current policies don’t change. As Tilotia writes “India’s inventory is concentrated in the north-western states of Punjab and Haryana, which store 36 million tons of its 66 million tons of stock. Given the large procurement expected from these states again this year (though Madhya Pradesh may better Haryana in wheat procurement this year, especially given state elections), this imbalance can worsen.”
Interestingly, the government can use this excess inventory of rice and wheat to control inflation and at the same time bring down its fiscal deficit. The government currently has rice and wheat worth in excess of Rs 60,000 crore. On the other hand it also has a disinvestment target of Rs 54,000 crore for the next financial year (i.e. the period between April 1, 2013 and March 31, 2014). The government hopes to earn this amount by selling stakes it holds in public sector units to the public.
Along similar lines the government can try selling the excess rice and wheat that it currently holds in the open market. This will help control food inflation with the excess government stock hitting the market. Food forms around 43% of the consumer price inflation number and so if food inflation comes down, the consumer price inflation is also likely to come down.
The challenge of course in doing this is two fold. The first being moving grains from Punjab, Haryana where more than half the inventory lies. The second is to ensure that the market prices of rice and wheat don’t collapse.
Also the current MSP system is not working. If the idea is to pay the citizens of this country to improve their living standards, the government may be better off paying them in cash, rather than paying them in this roundabout manner that creates inflation. This is simply because the current system drives up the price of food for everyone else and it doesn’t necessarily always benefit the farmers. The middleman continue to make the most money.
As Tilotia puts it “If such a payment indeed needs to be made, there is no point in raising prices for all in the system by adding it to the price of the grain: Simply pay the farmer whatever support you want to pay him/her. India is reaching a situation where, by using UID it would be able to send payments to farmers directly. Maybe it is time to re-couple wheat and rice prices with global prices – that can meaningfully reduce inflation in India.”
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on March 6,2013.
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek)
Why Subbarao can’t cut rates; only Chidambaram can
If politicians and corporates are to be believed then India’s much beleaguered economy can be put back on track only if the Reserve Bank of India(RBI) brought down interest rates. The finance minister P Chidambaram did not mince words when he said in an interview to The Economic Times that “reduction in interest rates will certainly help get us to 6.5% (economic growth).” In another article in the Business Standard several CEOs (including those of real estate firms) have come on record to say that the RBI should cut interest rates in order to revive the economy.
The RBI meets next on March 19. And both CEOs and politicians seem to be clamouring for a repo rate cut. Repo rate is the interest rate at which RBI lends to banks. So the logic is that once the RBI cuts the repo rate (as it did when the last time it met in late January) the banks will get around to passing that cut by bringing down the interest rates they charge on their loans. Given this people will borrow and spend more. They will buy more houses. They will buy more cars. They will buy more two wheelers. They will buy more consumer durables. Companies will also borrow and expand. All this borrowing and spending will revive the economic growth and the economy will grow at 6.5% instead of the 4.5% it grew at between October and December, 2012. And we will all live happily ever after.
Now only if life was as simple as that.
Repo rate at best is a signal from the RBI to banks. When it cuts the repo rate it is sending out a signal to the banks that it expects interest rates to come down in the time to come. Now it is up to the banks whether they want to take that signal or not. And turns out they are not.
Several banks have recently been raising interest rates on their fixed deposits. Of course, if banks are raising interest rates on their deposits, they can’t be cutting them on their loans, given money raised from deposits is used to fund loans. And hence interest rates on loans has to be higher than those on deposits. Banks have raised interest rates despite the fact that the RBI cut the repo rate by 25 basis points (one basis point is equal to one hundreth of a percentage) when it last met on January 29, 2013.
So why are banks raising interest rates when the RBI has given the opposite signal? The answer for that lies in the Economic Survey released on February 27, 2013. The gross domestic savings of the country were at 36.8% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) during the course of 2007-2008 (i.e. the period between April 1, 2007 and March 31, 2008). They had fallen to 30.8% of the GDP during the course of 2011-2012 (i.e. the period between April 1, 2011 and March 31, 2012). I wouldn’t be surprised if they have fallen further once figures for the current financial year become available.
The household savings (i.e. the money saved by the citizens of India) have also been falling over the last few years. In the year 2009-2010 (i.e. the period between April 1, 2009 and March 31, 2010) the household savings stood at 25.2% of the GDP. In the year 2011-2012, the household savings had fallen to 22.3% of the GDP.
What this means is that the country as a whole is saving lesser money than it was before. A straightforward explanation for this is the high inflation that has prevailed over the last few years. People are possibly spending greater proportions of their income to meet the rising expenses and that has lead to a lower savings rate.
Interestingly the financial savings have been falling at an even faster rate than overall savings. As the Economic Survey points out “Within households, the share of financial savings vis-à-vis physical savings has been declining in recent years. Financial savings take the form of bank deposits, life insurance funds, pension and provident funds, shares and debentures, etc. Financial savings accounted for around 55 per cent of total household savings during the 1990s. Their share declined to 47 per cent in the 2000-10 decade and it was 36 per cent in 2011-12. In fact, household financial savings were lower by nearly Rs 90,000 crore in 2011-12 vis-à-vis 2010-11.”
One reason for this (explained in the Economic Survey) is that a lot of savings have been going into gold. And why have the savings been going to gold? The government would like us to believe that it is our fascination for gold that is driving our savings into gold. But then our fascination for gold is not a recent phenomenon. Indians have always liked gold.
People buy gold as a hedge against inflation. When inflation is high the real returns on fixed income instruments are low. Real return is the difference between the rate of interest offered on let us say a fixed deposit, minus the prevailing rate of inflation.
As the Economic Survey puts it “High inflation reduces the return on other financial instruments. This is reflected in the negative correlation between rising(gold) imports and falling real rates.” (As can be seen from the following table).
What this means is that when inflation is high, the real return on fixed income investments like fixed deposits is low. Consumer Price Inflation has been close to 10% in India over the last few years. And this has meant that investment avenues like fixed deposits have been made unattractive, leading people to divert their savings into gold. “The overarching motive underlying the gold rush is high inflation…High inflation may be causing anxious investors to shun fixed income investments such as deposits and even turn to gold as an inflation hedge,” the Economic Survey points out.
What does this mean in the context of b
anks? It means that banks have had a lower pool of savings to borrow from. One because the overall savings have come down. And two because within overall savings the financial savings have come down at a much faster rate due to lower real rates of interest, after adjusting for inflation. This means that banks need to offer high rates of interest on their fixed deposits to make it attractive for people to deposit their money into banks. It is a simple case of demand and supply.
And who is the cause for all the inflation that the country has seen over the last few years and continues to see? Not you and me.
High inflation has been caused by the burgeoning subsidies provided by the government. The total subsidy in 2006-2007(i.e. The period between April 1, 2006 and March 31, 2007) stood at Rs 53,462.60 crore. This has gone up by nearly five times to Rs 2,57,654.43 crore for the year 2012-2013 (i.e. the period between April 1, 2012 and March 31, 2013).
All this expenditure of the government has landed up in the hands of people and created inflation. The Economic Survey admits to the same when it states “With the subsidies bill, particularly that of petroleum products, increasing, the danger that fiscal targets would be breached substantially became very real in the current year. The situation warranted urgent steps to reduce government spending so as to contain inflation.” So the Economic Survey equated the high government spending to inflation.
The subsidy bill for the year 2013-2014 (i.e. the period between April 1, 2013 and March 31, 2014) is expected to be at Rs 2,31,083.52 crore. This is number seems to be underestimated as this writer has explained before. And so the inflationary scenario is likely to continue.
Given that people will want to deploy their savings to other modes of investment rather than fixed deposits. And hence banks will have to continue offering higher interest rates to get people interested in fixed deposits.
As the Economic Survey points out “The rising demand for gold is only a “symptom” of more fundamental problems in the economy. Curbing inflation, expanding financial inclusion, offering new products such as inflation indexed bonds, and improving saver access to financial products are all of paramount importance.”
To conclude, there is very little that the D Subbarao led RBI can do to push down interest rates. In fact interest rates are totally in the hands of the government. If the government can somehow control inflation, interest rates will start to come down automatically. For that to happen subsidies in particular and the high government expenditure in general, will have to be controlled. And that is not going to happen anytime soon.
The article originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on March 4, 2013
(Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets at @kaul_vivek)
Why the foreigners are not impressed with Budget 2013
 The foreigners aren’t impressed with the budget presented by Finance Minister P Chidambaram yesterday. These include the rating agencies as well as investors who pour money into the Indian stock market.
The foreigners aren’t impressed with the budget presented by Finance Minister P Chidambaram yesterday. These include the rating agencies as well as investors who pour money into the Indian stock market.
As Ruchir Sharma, head of the Emerging Markets Equity team at Morgan Stanley Investment Management and the author of Breakout Nations told NDTV in a discussion yesterday: “On the fiscal side..a lot of the assumptions are being torn apart when people are analysing this budget.”
Government income is essentially categorised into two parts. Revenue receipts and capital receipts. Revenue receipts include regular forms of income which the government earns every year like income tax, corporate tax, excise duty, customs duty, service tax and so on.
Capital receipts include money earned through sale of shares in government-owned companies, telecom spectrum, etc. Capital receipts are essentially earned by selling things that the government owns. Once something is sold it can’t be sold again and that is an important point to remember. Borrowing by the government, which is not an income, is also comes under capital receipts.
Revenue receipts for the year 2013-2014 are expected to be at Rs 10,56,331 crore. For the year 2012-2013 revenue receipts were budgeted to be at Rs 9,35,685 crore when the last budget was presented. This number has now been revised to Rs 8,71,828 crore. Hence, the government expects the revenue receipts to grow by 21.2 percent in 2013-2014. This projection has been made in an environment where the government is unlikely to meet its original revenue receipts target for the year. Also the revenue receipts this year will grow by 16 percent in comparison to last year.
So a 21 percent growth in revenue receipts is a fairly optimistic assumption to make. So if revenues collected are lower during the course of the year and the expenditure continues at the same rate, the fiscal deficit will be higher than it has been projected to be. Or expenditure will have to be cut, like it has been done this year. And that is not always a good sign.
Another point that this writer made yesterday was on the side of subsidies. For the year 2012-2013 subsidies were expected to be at Rs 1,90,015 crore. This has been revised to Rs 2,57,654 crore, which is almost 36 percent higher. This makes it very difficult to believe next year’s subsidy target of Rs 2,31,084 crore, especially when more subsidies/sops are likely to be announced during the course of the next financial year in view of the 2014 Lok Sabha elections.
As I said in the piece, the understating of subsidies has not been a one-off thing and has happened every year during the second term of the Congress-led United Progressive Alliance (UPA) government. So higher subsidies than budgeted might again mean a higher fiscal deficit or a cut in expenditure.
Amay Hattangadi and Swanand Kelkar of Morgan Stanley Investment Management, in a report titled The Art of Balancing, make an interesting point. They feel that the finance minister by projecting a fiscal deficit of 5.2 percent of GDP for this financial year and 4.8% of GDP might be giving an impression of fiscal prudence, but a closer look at the math reveals a different story.
As they write: “As trained accountants, we have learnt that sale of assets from the balance-sheet are one-off or non-recurring items. It is interesting that if we add back the estimates from sale of (telecom) spectrum and divestment of government companies (both non-recurring in our view), the ‘real’ fiscal deficit/GDP ratio for financial year 2014 shows no improvement over financial year 2013.”
The table below sourced from the Morgan Stanley report gives the complete story.

Table from Morgan Stanley
Once we take away capital receipts like divestment of shares and sale of telecom spectrum, which are essentially one-off sources of income from the equation, the real fiscal deficit to GDP ratio comes in at a more realistic 5.6 percent of the GDP and not 4.8 percent or 5.2 percent that it has been projected to be. The point is that people aren’t buying the numbers put out in Chidambaram’s budget.
There is also very little acknowledgement of the mistakes that have made by the government over the past few years.
Ruchir Sharma, in his discussion on NDTV, put up a very interesting slide. The slide shows that India has consistently held rank 24-26 among 150 emerging market countries when it comes to economic growth over the last three decades. We thought we were growing at a very fast rate over the last few years, but so was everyone else. As Sharma put it: “The last decade we thought we had moved to a higher normal and it was all about us. Every single emerging market in the world boomed and the rising tide lifted all boats, including us.”

India’s growth has remained consistent in the last three decades
But now that we are not growing as fast as we were in the past, it is because of the slowing down of the global economy. As Chidambaram put it in his budget speech “We are not unaffected by what happens in the rest of the world and our economy too has slowed after 2010-11.”
Sharma pointed out the self-serving nature of this argument thus: “When the downturn happens it is about the global economy. When we do well it’s about us.” This is a disconnect that still persists, as is evident from Chidambaram’s statement.

India in the last four years was fed with artificial fiscal stimulas, which led to high inflation
Another slide put up by Sharma makes for a very interesting reading. “Between 2008 and 2010 we implemented a massive stimulus, both fiscal and monetary, and that artificially inflated our growth rate to 13th in emerging market (as is evident from the slide). We were thrilled about it. It led to a massive increase in inflation and now this is payback time. Between 2010-2012, we fell to the 40th position,” said Sharma. So as more money was pumped into the economy, it chased the same number of goods and services, which led to higher prices or inflation.
So the massive spending by the government came back to haunt us. Inflation went through the roof. India’s rank among emerging markets when it came to inflation used to be around 60th. In the last few years it has fallen to the 118-119th position.

As Sharma puts it: “This is the problem that India has today. India does not have an explicit inflation target. Most emerging markets and central banks work with explicit inflation targets. We have gotten away with it. I think the time is coming now for a more rules-based system. If we had an inflation target I doubt if we would have allowed inflation to increase at such a rapid pace”
Nations which have grown in the past at rapid rates have never had consistently high inflation. “And whenever inflation persisted over a period of time it always meant that the economy was headed for a major slowdown,” said Sharma. High inflation continues to be a major reason for worry in India.
Inflation in India has been a manifestation of a rapid increase in government spending. The total expenditure of the government in 2006-2007 was at Rs 5,81,637 crore. For the year 2013-2014, the total expenditure is expected to be at Rs 16,65,297 crore. The expenditure thus has nearly tripled (actually it’s gone up 2.9 times). During the same period the revenue receipts of the government have gone up only 2.5 times. The difference, as we all know, has been made up by borrowing leading to a burgeoning fiscal deficit. The next slide tells you how hopeless the situation really is.

So India is really at the bottom when it comes to the fiscal deficit.
The point is very basic. We don’t earn all the money that we want to spend. As Chidambaram admitted to in the budget speech: “In 2011-12, the tax GDP ratio was 5.5 percent for direct taxes and 4.4 percent for indirect taxes. These ratios are one of the lowest for any large developing country and will not garner adequate resources for inclusive and sustainable development. I may recall that in 2007-08, the tax GDP ratio touched a peak of 11.9 percent.”
And this budget highlighted very little on how the government plans to increase its revenue receipts. In fact, Chidambaram even admitted that only 42,800 individuals admitted to having taxable incomes of greater than Rs 1 crore in India. This is a situation that needs to be set right. More Indians need to be made to pay income tax.
To conclude, let me say that the foreigners are worried and so should we.
The aritcle originally appeared on www.firstpost.com on March 1, 2013.
Vivek Kaul is a writer. He tweets @kaul_vivek